- Who Discovered The Law Of Conservation Of Matter?
- Did Lavoisier discover the law of conservation of matter?
- Did Albert Einstein discover the law of conservation of energy?
- Who founded the conservation of energy?
- How did Lavoisier discover the law of conservation of mass?
- What did John Dalton discover?
- What did Antoine Lavoisier discover?
- How did Julius Robert Mayer discovered the law of conservation of energy?
- Who discovered the first law of thermodynamics?
- Who said energy Cannot be created?
- Where is law of conservation of energy?
- What is the name given to energy conservation law in thermal physics?
- What does the law of conservation of matter state?
- Who discovered the law of multiple proportions?
- What did Antoine Lavoisier discovered about the atomic theory?
- What did Rutherford discover?
- What was JJ Thomson discovery?
- What did Thomson discover?
- Who discovered hydrogen?
- Who discovered chemistry?
- Who is known as Father of Chemistry Why?
- What was the observation of Julius von Mayer 18th century?
- Who discovered energy efficiency?
- Who is father of thermodynamics?
- Who contributed the second law of thermodynamics?
- Where was the first law of thermodynamics discovered?
- What did Einstein say about electricity?
- Who wrote the laws of thermodynamics?
- Who put forward the law of conservation of mass?
- What is the law of conservation of matter and energy?
- Who said that matter Cannot be created or destroyed?
- Which statement is true about the law of conservation of energy?
- Which is the first law of thermodynamics?
- What is the second law of thermodynamics called?
- Related Articles
Who Discovered The Law Of Conservation Of Matter?
Antoine Lavoisier’s
Did Lavoisier discover the law of conservation of matter?
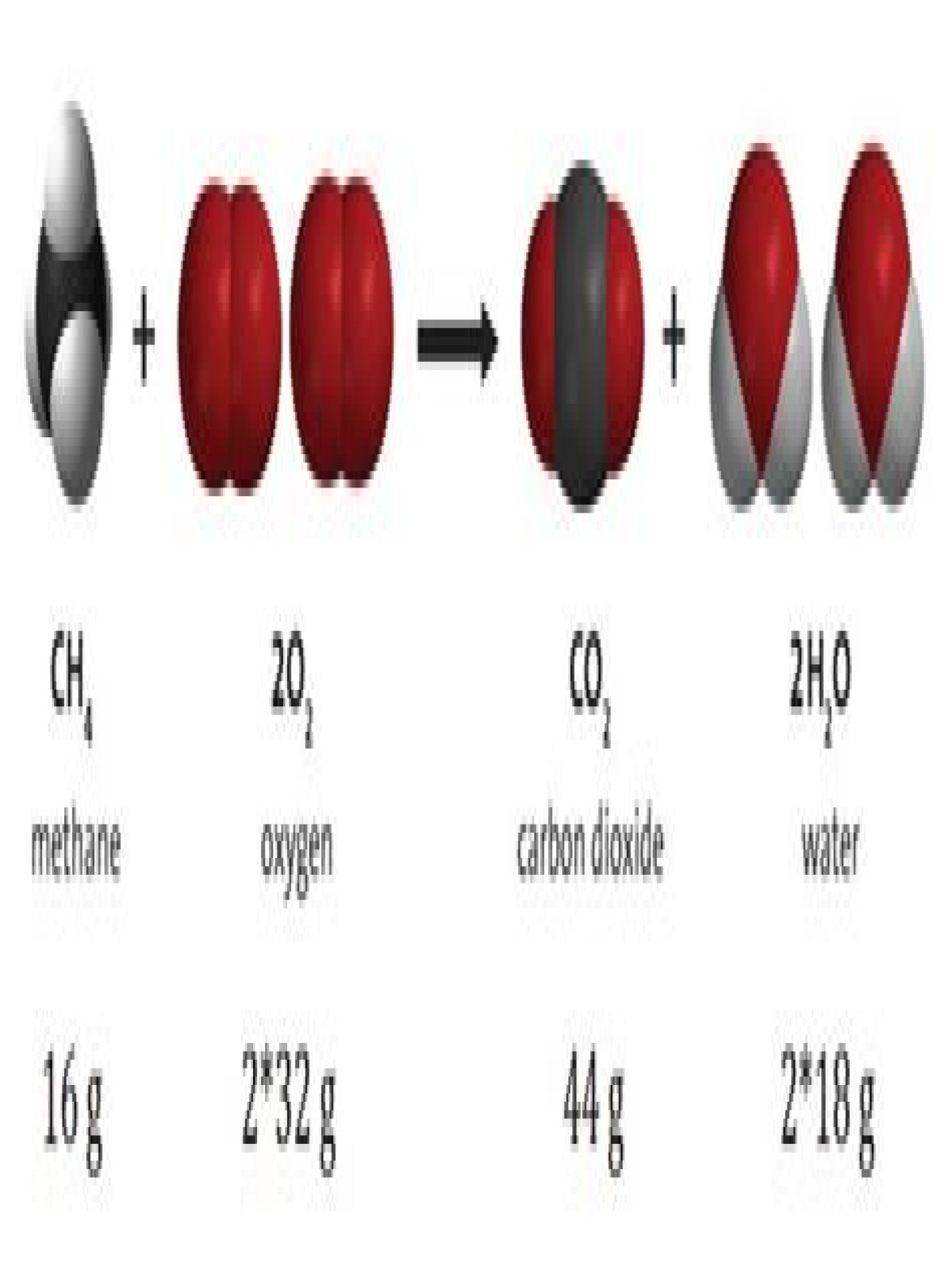
Lavoisier. The first breakthrough in the study of chemical reactions resulted from the work of the French chemist Antoine Lavoisier between 1772 and 1794. … His results led to one of the fundamental laws of chemical behavior: the law of conservation of matter, which states that matter is conserved in a chemical reaction.
Did Albert Einstein discover the law of conservation of energy?
Conservation of energy (the First Law of Thermodynamics) is a simple law stating that although energy may change form, it cannot disappear altogether, nor can it be created. ) discovered by Einstein. This new law is called the law of conservation of mass and energy.
Who founded the conservation of energy?
Julius Robert von MayerBetween 1842and 1847, Julius Robert von Mayer, James Prescott Joule, and Hermann Ludwig Ferdinand von Helmholtz discovered and formulated the basics of what we refer to today as the law of conservation of energy: Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be transformed from one form to another.
How did Lavoisier discover the law of conservation of mass?
What did John Dalton discover?
What did Antoine Lavoisier discover?
How did Julius Robert Mayer discovered the law of conservation of energy?
Who discovered the first law of thermodynamics?
Rudolf Clausius
Who said energy Cannot be created?
Albert Einstein
Where is law of conservation of energy?
The law of conservation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed – only converted from one form of energy to another. This means that a system always has the same amount of energy, unless it’s added from the outside.
What is the name given to energy conservation law in thermal physics?
The First Law of Thermodynamics (Conservation) states that energy is always conserved, it cannot be created or destroyed. In essence, energy can be converted from one form into another.
What does the law of conservation of matter state?
Who discovered the law of multiple proportions?
John Dalton
What did Antoine Lavoisier discovered about the atomic theory?
What did Rutherford discover?
What was JJ Thomson discovery?
What did Thomson discover?
On April 30, 1897, British physicist J.J. Thomson announced his discovery that atoms were made up of smaller components. This finding revolutionized the way scientists thought about the atom and had major ramifications for the field of physics.
Who discovered hydrogen?
Hydrogen/DiscoverersHydrogen was discovered by the English physicist Henry Cavendish in 1766. Scientists had been producing hydrogen for years before it was recognized as an element. Written records indicate that Robert Boyle produced hydrogen gas as early as 1671 while experimenting with iron and acids.
Who discovered chemistry?
Who is known as Father of Chemistry Why?
The title of Father of Chemistry is acquired by Antoine Lavoisier, who listed elements, described properties of matter, helped to revise and standardize chemistry nomenclature and made a host of other contribution to the field of chemistry. … He is credited with establishing mass conservation in chemical reactions.
What was the observation of Julius von Mayer 18th century?
The observation led Mayer to speculate about the conversion of food to heat in the body, and also the fact that the body can do work. He came to the view that heat and work are interchangeable – that the same amount of food can be converted to different proportions of heat and work, but the total must be the same.
Who discovered energy efficiency?
Arthur H. Rosenfeld
Who is father of thermodynamics?
Nicolas Léonard Sadi CarnotNicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot is often described as the “Father of Thermodynamics.”Apr 10, 2012
Who contributed the second law of thermodynamics?
Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot was a French physicist, who is considered to be the “father of thermodynamics,” for he is responsible for the origins of the Second Law of Thermodynamics, as well as various other concepts.
Where was the first law of thermodynamics discovered?
What did Einstein say about electricity?
“Energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be changed from one form to another.”
Who wrote the laws of thermodynamics?
“The first established principle of thermodynamics (which eventually became the Second Law) was formulated by Sadi Carnot in 1824. By 1860, as found in the works of those as Rudolf Clausius and William Thomson, there were two established “principles” of thermodynamics, the first principle and the second principle.
Who put forward the law of conservation of mass?
What is the law of conservation of matter and energy?
The law of conservation of mass states that in a chemical reaction mass is neither created nor destroyed. … The carbon atom changes from a solid structure to a gas but its mass does not change. Similarly, the law of conservation of energy states that the amount of energy is neither created nor destroyed.
Who said that matter Cannot be created or destroyed?
Antoine LavoisierAntoine LavoisierA portrait of Antoine Lavoisier, the scientist credited with the discovery of the law of conservation of mass. This law states that, despite chemical reactions or physical transformations, mass is conserved — that is, it cannot be created or destroyed — within an isolated system.
Which statement is true about the law of conservation of energy?
Answer Expert Verified The statement that is true according to the law of conservation of energy is D. Energy cannot be destroyed, as it will always be present in some form or another. Energy can be converted from one form to another, and thus it will always exist without being destroyed.
Which is the first law of thermodynamics?
The first law of thermodynamics, also known as Law of Conservation of Energy, states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed; energy can only be transferred or changed from one form to another.